Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Sample Inventory Management System for Managing Biological and Cell Therapy Samples

Across the highly regulated landscape of life sciences, properly managing biological and cell therapy samples isn’t just good practice, it’s essential for regulatory compliance, patient safety, and research integrity. Yet many organizations continue to rely on manual inventory systems that create significant risks and inefficiencies.
This comprehensive guide walks through the challenges of manual inventory systems, highlights the key benefits of sample inventory management systems, and offers a clear, actionable 7-phase implementation roadmap.
The Limitations of Manual Sample Inventory
Traditional inventory management for biological samples typically relies on spreadsheets, paper logs, or basic database systems. These approaches present several critical challenges
- Error-prone data entry: Manual transcription creates opportunities for mistakes that can compromise sample integrity
- Limited traceability: Spreadsheets struggle to maintain proper Chain of Custody (COC) and Chain of Identity (COI) documentation
- Difficult auditability: During FDA inspections, retrieving complete sample histories becomes time-consuming and stressful
- Siloed information: Data trapped in disconnected systems prevents organization-wide visibility
- Inefficient sample retrieval: Locating specific samples becomes increasingly difficult as inventory grows
- Poor scalability: Manual systems buckle under the weight of expanding operations
- Compliance risks: GMP requirements demand more robust tracking than spreadsheets can provide
“According to recent industry data, laboratories using manual systems spend 10–15 hours/week on admin tasks and see 4–5x more retrieval errors than those using electronic systems, a gap that becomes even clearer when you compare spreadsheets vs. sample inventory management systems.” |
8 Critical Automation Tasks of a Sample Inventory Management System
Modern Sample Inventory Management Systems perform several crucial functions that transform biological sample management
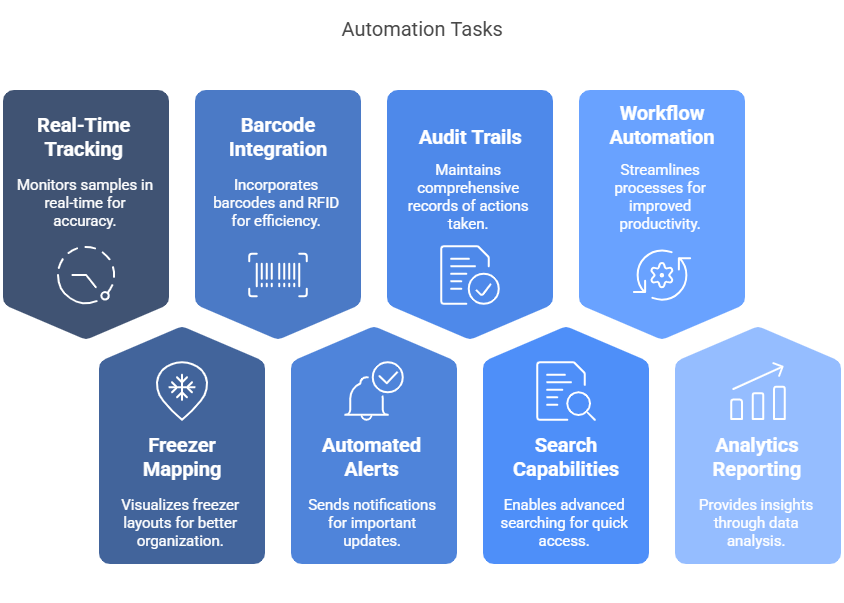
1. Real-Time Sample Tracking – Maintain comprehensive digital records of every sample’s location, status, and movement history fulfilling regulatory Chain of Custody and Identity requirements essential for FDA compliance.
2. Freezer Mapping and Visualization: Visually mirror your physical storage environment (racks, boxes, shelves) so technicians can instantly find samples or storage space.
3. Barcode and RFID Integration: Reduce manual errors and save time by scanning samples. Each scan updates the system with the sample’s new status and location information maintaining data integrity throughout the process.
4. Automated Alerts and Notifications: Get notified in real-time for expiration dates, temperature excursions, maintenance schedules, quality checks and low inventory levels.
5. Comprehensive Audit Trails: Automatically log every user action and change, creating an immutable record for compliance teams. These detailed records serve as a key element of traceability and audit readiness which proves invaluable during FDA inspections and internal quality reviews.
6. Advanced Search Capabilities: Unlike spreadsheets, advanced sample inventory management systems allow complex, multi-parameter searches across the entire inventory. This functionality drastically reduces the time needed to locate samples based on specific criteria like patient ID, collection date, or processing status.
7. Workflow Automation: Embed Standard operating procedures (SOPs) can be built directly into the system, guiding technicians through proper sample handling protocols and documentation requirements. This standardization ensures consistent compliance with GMP regulations, and aligns with common regulatory compliance checks for biological sample storage.
8. Analytics and Reporting – Generate customizable reports that provide insights into inventory utilization, sample status distribution, and operational efficiencies. These analytics support to improve sample recalls, deviations, and CAPA response as well as data-driven decision-making.
Implementation Guide: Transition to a Sample Inventory Management System in 7 Phases
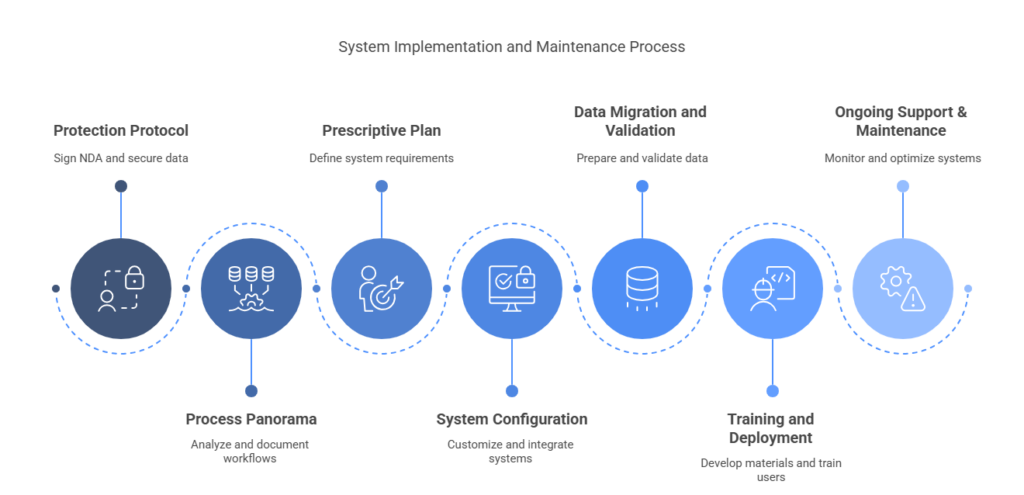
Phase 1: Protection Protocol (NDA) – Initiating implementation begins with safeguarding confidentiality. Signing an NDA ensures that proprietary data, workflows, and documentation remain protected throughout the process.
Phase 2: Process Panorama (Workflow Study) – A detailed analysis of existing sample workflows is essential to identify inefficiencies and compliance risks. This stage includes evaluating current processes, mapping data touchpoints, and outlining stakeholder responsibilities.
Phase 3: Prescriptive Plan (Proposal) – With a clear understanding of needs, the system’s functional scope is defined. This includes outlining integrations, audit requirements, user access levels, and measurable success indicators such as improved traceability and time savings required to scale operations from Phase I to commercialization
Phase 4: System Configuration – This phase focuses on aligning the system setup with your physical infrastructure and compliance needs. A digital model of freezer layouts is created, sample types and storage hierarchies are defined, and user access roles are set. Compliance features such as audit trails and electronic signatures are enabled. Integrations with platforms like LIMS or ELNs are considered to support unified operations.
Phase 5: Data Migration and Validation – This phase involves cleaning legacy records, applying qualification protocols (IQ, OQ, PQ), and compiling validation documentation to support future audits.
Phase 6: Training and Deployment – This phase focuses on preparing internal users with guides, training sessions, and demonstrations tailored to their roles. A staged rollout approach enables early feedback and smoother adoption across teams.
Phase 7: Ongoing Support & Maintenance – Post-implementation, the focus shifts to continuous improvement. Ongoing monitoring, regular workflow reviews, and timely system validation help maintain compliance and ensure the system evolves alongside operational needs.
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators
After implementation, track these metrics to evaluate system effectiveness:
- Sample retrieval time: Average time to locate and access samples
- Documentation accuracy: Percentage of records with complete, error-free documentation
- Audit preparedness: Time required to produce requested documentation during audits
- Storage optimization: Percentage of storage space efficiently utilized
- Error reduction: Number of sample management incidents or deviations
- User adoption : System usage rates and user satisfaction scores
Conclusion
Sample inventory management systems don’t just modernize operations, they redefine how life sciences organizations maintain compliance and protect sample integrity. Organizations like New York Blood Centers (NYBC) have already made this transition successfully, integrating a compliant, scalable sample inventory management system to manage high-stakes cord blood operations without compromising on traceability or audit readiness. Looking to transform your biological sample management with a sample inventory management system? Contact our experts for a personalized demonstration of PragLife’s Sample Inventory Management Module.



